静态编译
不同于动态编译是将应用程序需要的模块都编译成动态链接库,启动程序(初始化)时,这些模块不会被加载,运行时用到哪个模块就调用哪个。静态编译就是在编译时,把所有模块都编译进可执行文件里,当启动这个可执行文件时,所有模块都被加载进来,反映在现实中就是程序体积会相对大一些,在 IDA 中会发现所有用到函数都是静态编译好的
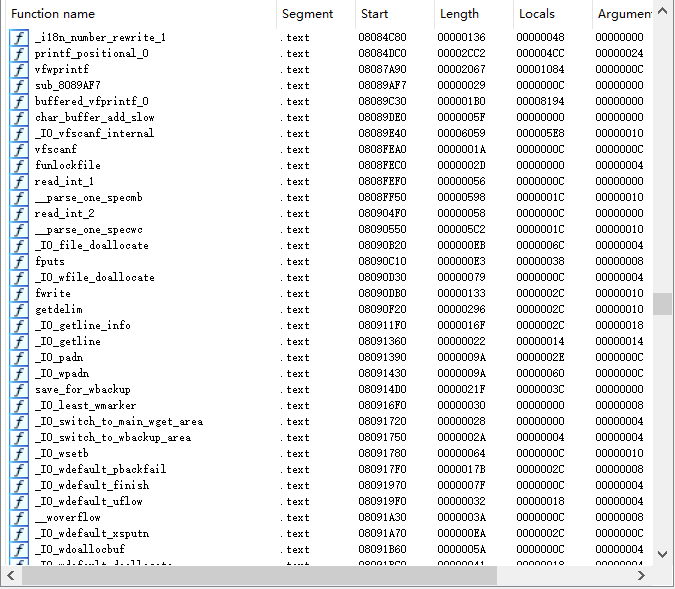
我们先检查一下文件:
syc@ubuntu:~/Desktop/TEMP$ checksec 13_angr_static_binary
[*] '/home/syc/Desktop/TEMP/13_angr_static_binary'
Arch: i386-32-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x8048000)拖进 IDA 查看一下函数:
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
signed int i; // [esp+1Ch] [ebp-3Ch]
signed int j; // [esp+20h] [ebp-38h]
char s1[20]; // [esp+24h] [ebp-34h]
char s2[4]; // [esp+38h] [ebp-20h]
int v8; // [esp+3Ch] [ebp-1Ch]
unsigned int v9; // [esp+4Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v9 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
print_msg();
for ( i = 0; i <= 19; ++i )
s2[i] = 0;
*(_DWORD *)s2 = 'NVJL';
v8 = 'UAPE';
printf("Enter the password: ");
_isoc99_scanf("%8s", s1);
for ( j = 0; j <= 7; ++j )
s1[j] = complex_function(s1[j], j);
if ( !strcmp(s1, s2) )
puts("Good Job.");
else
puts("Try again.");
return 0;
}int __cdecl complex_function(signed int a1, int a2)
{
if ( a1 <= 64 || a1 > 90 )
{
puts("Try again.");
exit(1);
}
return (37 * a2 + a1 - 65) % 26 + 65;
}通常,Angr 会自动地用工作速度快得多的 simprocedure 代替标准库函数,但是这题中库函数都已经因为静态编译成了静态函数了,angr 没法自动替换。要解决这题,需要手动 Hook 所有使用标准库的 C 函数,angr 已经在 simprocedure 中为我们提供了这些静态函数, 这里列举一些常用的函数
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['malloc']
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['fopen']
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['fclose']
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['fwrite']
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['getchar']
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['strncmp']
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['strcmp']
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['scanf']
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['printf']
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['puts']
angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['exit']我们只需要手动找到程序中用到静态函数的地址,将其利用 simprocedure 提供的函数 Hook 掉即可
话不多说上 EXP:
import angr
import claripy
import sys
def Go():
path_to_binary = "./13_angr_static_binary"
project = angr.Project(path_to_binary, auto_load_libs=False)
initial_state = project.factory.entry_state()
project.hook(0x804ed40, angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['printf']())
project.hook(0x804ed80, angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['scanf']())
project.hook(0x804f350, angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['puts']())
project.hook(0x8048d10, angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['glibc']['__libc_start_main']())
simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state, veritesting=True)
def is_successful(state):
stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(1)
if b'Good Job.\n' in stdout_output:
return True
else:
return False
def should_abort(state):
stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(1)
if b'Try again.\n' in stdout_output:
return True
else:
return False
simulation.explore(find=is_successful, avoid=should_abort)
if simulation.found:
for i in simulation.found:
solution_state = i
solution = solution_state.posix.dumps(0)
print("[+] Success! Solution is: {0}".format(solution))
#print(scanf0_solution, scanf1_solution)
else:
raise Exception('Could not find the solution')
if __name__ == "__main__":
Go()运行一下查看结果:
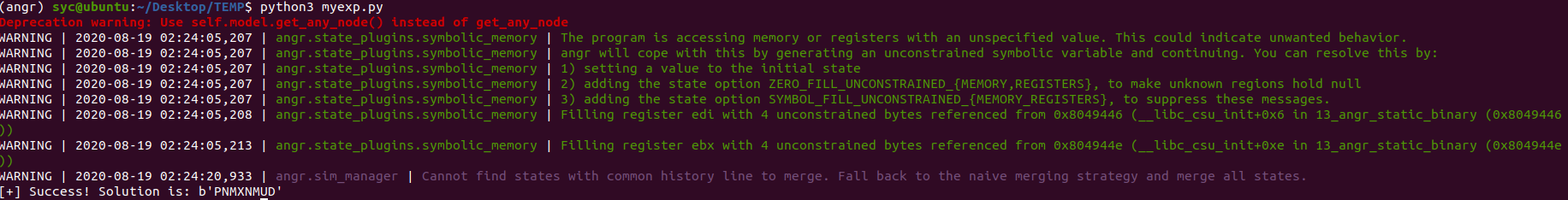
这题解题真正需要用的函数也就 printf,scnaf,puts,即完成了 angr 需要的输出、输入、路径选择的功能,我们手动找到这几个函数的地址

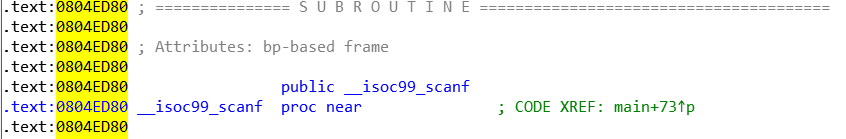
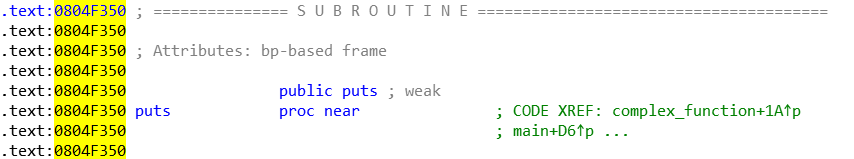
这里比较容易忽略的一个函数就是 __libc_start_main
让我们回忆一下在 linux 下一个 c 程序是如何启动的:
- execve 开始执行
- execve 内部会把 bin 程序加载后,就把. interp 指定的动态加载器加载
- 动态加载器把需要加载的 so 都加载起来,特别的把 libc. so. 6 加载
- 调用到 libc. so. 6 里的 __libc_start_main 函数,真正开始执行程序
- libc_start_main 做了一些事后,调用到 main () 函数
所以程序是一定需要用到 __libc_start_main,分析后得到地址:0x8048D10,于是得到代码:
project.hook(0x804ed40, angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['printf']())
project.hook(0x804ed80, angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['scanf']())
project.hook(0x804f350, angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc']['puts']())
project.hook(0x8048d10, angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['glibc']['__libc_start_main']())其它的部分和之前做过的 02_angr_find_condition 一致,不再赘述